Inguinofemoral Lymphnode Dissection
Read the rest with a free account on Gynaefellow
Author
Preparation & setup
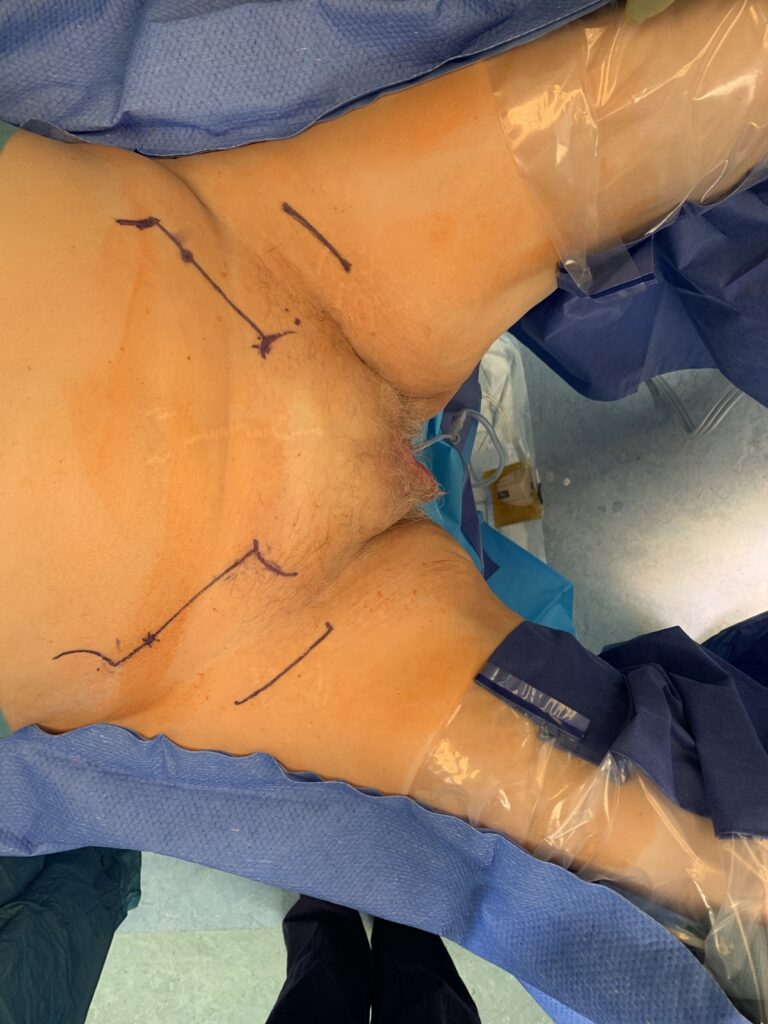
- Positioning
- Patient in modified lithotomy position
- Draping
- Upper: 2 cm above ASIS and across the abdomen
- Lower: 5-10 cm from the knee
- Under buttocks
- Foleys catheter
- Instruments
- Monopolar needle
- Colorado needle for skin, usual needle to other
- Energy set up: cut 35-pure, coagulation 35-spray
- Short bipolar scissors
- Advanced bipolar device
- Skin retractors; Kilner (Cat-Paw), Langenbecks (medium and large)
- Monopolar needle
- Drain
- Redivac drain size 10
Patient position and incision planning
- Patient is placed in supine position with gluteal fold at the end of the table.
- The patient is in modified lithotomy position with legs slightly abducted.
- Draw a line between the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and pubic tubercle
- Measure 3 cm, medial to ASIS to mark your lateral dissection border (By doing this step you minimise injury to the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh).
- Draw a 90-degree line, 6-7 cm down towards the thigh (The end point is about 1-2 cm below the groin crease).
- Repeat the same step from the pubic tubercle.
- Join the two-end point; this would represent your incision for the groin nodes.
Access and identification of dissection plans
- Skin incision is carried out using Colorado monopolar needle (pure cut).
- Once in the subcutaneous, use bipolar energy and gently until you reach to superficial fascia (Campers fascia).
- Incise the fascia gently and using the Cat-Paw retractors left the fascia and dissect parallel to the lower border of the fascia to separate the superficial inguinal nodes from the subcutaneous tissue.
- Ensure Campers fascia remains intact to obtain primary wound healing and avoid skin break down.
- Continue with the dissection until the inguinal ligament is reached.
Dissection Superficial inguino-femoral lymph nodes
- Upper border: Dissect the superficial inguinal lymph nodes off the inguinal ligament starting from the upper edge of the ligament down to the femoral triangle.
- Be aware of
- Lateral circumflex vessels laterally
- Superficial epigastric vessels central & cranial
- Lateral border: Dissect the lymph-nodes off the sartorius muscle fascia starting from upper down to the lower border of the triangle.
- Medial border: Dissect the lymph nodes off the adductor longus muscle
- Be aware of the superficial external pudendal vessels
- Once the borders identified proceed with separating/dissecting the groin nodes off the femoral triangle floor proceeding from lateral to medial.
- Identify the great saphenous vein and dissect carefully until the point of insertion with the femoral vein.
- Complete the dissection and retrieval of the superficial lymph nodes.
- Be aware of
Dissection deep femoral lymph nodes
- Usually these are 1-3 lymph nodes present in fossa ovalis
- Gently dissect the fatty tissue starting from the point of junction between great saphenous vein and femoral vein. Follow the femoral vein through the length of fossa ovalis (usually 3 cm)
- Retract the inguinal ligament cephalad to check for Cloquet’s node.
Drain & closure
- Place the drain on the pelvic floor (fenestrated tip away from vessels)
- Use silk suture to fix the drain
- This step is used to reduce risk of drain detaching prematurely
- Close Campers fascia with interrupted sutures vicryl 2/0
- Close skin subcut with continuous suture
- Steristerips to skin
- Chloramphenicol
